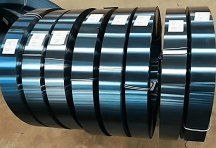
60Si2MnA Spring Steel
Short Description:
60Si2MnA strength, hardness, elasticity and hardenability are higher than 65mn steel, with the tendency of overheating sensitivity and temper brittleness, water quenching tend to form cracks. Annealing Machinability is acceptable, low cold plastic deformation, poor weldability. Loaded by the medium plate spring, coil diameter of 7-20mm and spring washers. Spring ring. High wear-resistant parts, such as grinding machine spindle. Spring chuck. Precision machine screw. Cutter. Helical roller bea...
Product Detail
FAQ
Product Tags
60Si2MnA strength, hardness, elasticity and hardenability are higher than 65mn steel, with the tendency of overheating sensitivity and temper brittleness, water quenching tend to form cracks. Annealing Machinability is acceptable, low cold plastic deformation, poor weldability. Loaded by the medium plate spring, coil diameter of 7-20mm and spring washers. Spring ring. High wear-resistant parts, such as grinding machine spindle. Spring chuck. Precision machine screw. Cutter. Helical roller bearings on the ring. Railway rails.
Chemical Composition:
| C(%): | SI(%): | Mn(%): | S (%): | P (%): | Cr(%): | Ni(%): | Cu(%): | V(%): |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.54~0.60 | 1.5~2.0 | 0.70~1.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.35 | ≤0.35 | ≤0.25 | 0.08~0.16 |
Processing standard:
When the steel is used as the main part of the mold, it must be forged first to avoid longitudinal cracks. However, in order to eliminate the stress after forging and make the internal carbides of the steel uniform, spheroidizing annealing must be carried out to improve the service life of the die steel. However, the steel does not need to undergo spheroidizing annealing when used in the manufacture of springs.
If the rapid spheroidizing process heat treatment is used to replace the traditional spheroidizing annealing process, the spheroidizing structure can be more uniform, the spheroidizing rate can be improved, the product quality can be improved, and the production cycle can be shortened by half. The use of low-carbon martensite for high temperature quenching is beneficial to prolong the life of the cold work die.
The Ms point of the steel can be increased by increasing the austenitizing temperature to obtain more low-carbon martensite structure, improve the strength and toughness of the mold, and have higher fracture toughness, impact toughness and excellent wear resistance. . After quenching and tempering, the mold hardness is 58HRC, and the metallographic structure is lamellar tempered martensite + retained austenite, which is highly sensitive to microcracks, so the toughness is low, and it is easy to fracture during use.
Compared with ordinary quenching, the hardness obtained by the austempering process is only 1HRC, but the bending strength and toughness are suddenly greatly improved.
Cold-pressed blank softening treatment specification: temperature 740~760℃, holding time 4~6h, cooling rate of 50~100℃/h, temperature drop with furnace to ≤600℃, air cooling out of the furnace. Hardness ≤255HBS before treatment, treatment After hardness ≤217HBS.
Quenching and tempering specifications:
quenching temperature 870±10℃, oil cooling; tempering temperature 480℃±10℃.
Specification for austempering and tempering:
temperature 870℃, heat preservation 20min, oil cooling out of the furnace, immediately put it in a nitrate salt bath of 250℃ for 20 min, and air cooling out of the furnace.
Best heat treatment specification:
Preliminary heat treatment: 870°C oil quenching-790°C heating and holding for 25min-quenching to 680°C and holding 40min-furnace cooling to 500°C and air cooling.
Final heat treatment process:
quenching temperature 870℃, isothermal temperature 250℃, isothermal time 20min.
Critical point temperature (approximate value) Ac1=755℃, Ac3=810℃, Ar3=770℃, Ar1=700℃, Ms=305℃.
Hot working specification:
the initial forging temperature is 1100℃, and the final forging temperature is 850℃.
FAQ Content
![[0{7)7UAZ(]4W{5TSMC65Q7](https://www.htsteelmill.com/uploads/077UAZ4W5TSMC65Q7.png)